TOPPAN Establishes Method of Quantifying Simple Qualitative Test Results through Digital Image Color Management Techniques
Press release from the issuing company
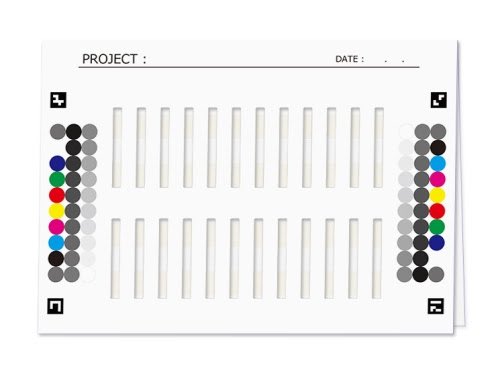
Mount with dedicated color chart
©TOPPAN Inc.
Constructing a quick and easy quantification method with Dai Nippon Toryo’s immunochromatography kit for exosome detection
Tokyo – TOPPAN Inc. (TOPPAN), a TOPPAN Group company and wholly owned subsidiary of TOPPAN Holdings Inc., has developed a method that harnesses color management techniques to quantify the results of simple immunochromatography1 testing data converted into digital imagery. Using this method, it is now possible to digitize and quantify the number of extracellular vesicles (exosomes)2 detected using Exorapid-qIC™, the world’s first commercial immunochromatography kit for exosome detection, which was developed by Dai Nippon Toryo Co., Ltd. (DNT).
TOPPAN harnessed its color management techniques to standardize display colors to create a method that quantifies data gathered through immunochromatography. By expanding the scope of what this technique can target from not only exosomes but also to various viruses and proteins, TOPPAN has made it possible to expand the use of immunochromatography into new areas and increase its value, also potentially helping increase the efficiency of academic research into exosomes and contributing to the development of diagnostic pharmacology and preventive medicine.
Background
Cancer (malignant neoplasms) continues to be the leading cause of death in Japan, and in recent years, greater importance has been placed on cancer prevention as well as on early diagnosis and treatment. It has been discovered that exosomes, a type of extracellular vesicle generated and released by human cells, contain information about the cells from which they originate, and that they are present in blood, urine, and many other body fluids. There are now high expectations for the development of simple testing technologies that detect exosomes in body fluids to support early diagnosis of cancer, dementia, and other diseases.
In addressing this, TOPPAN has applied its liquid biopsy3 exosome detection method to develop and patent an exosome detection technology using immunochromatography, and provided DNT with a license to use this technology in the design, development, fabrication, and sale of testing and reagent kits for experiments and research into exosomes. DNT used this technology to develop its Exorapid-qIC™ Immunochromatography Kit for Extracellular Vesicles, and it began selling the kit for use in research on July 25, 2023.
Immunochromatography is widely used in diagnostic virus testing for COVID-19 and influenza, but it is rarely used in quantitative testing due to the difficulty in digitizing and quantifying the amount of virus present.
To address this issue, TOPPAN has harnessed the color management techniques it has cultivated in the printing business over the years to develop CAM-FIT®,4 a technology that adjusts the colors of images taken with cameras to provide consistent colors across different displays, printers, printed matter, and other devices and material. This makes it possible to adjust photographic data such that the colors are displayed correctly independent of initial lighting conditions and imaging equipment. Using this technique, it is now possible to digitize immunochromatography detection data without depending on the lighting conditions or cameras used when obtaining the data. In collaboration with DNT, TOPPAN has confirmed that this technique can be used to digitize and quantify data obtained through exosome immunochromatography.
?
TOPPAN will continue to use its color management technologies to expand the use of immunochromatography into new areas and give it new value, while simultaneously contributing to the development of academic research into exosomes.
Features
1) Use of dedicated color chart improves analysis accuracy and efficiency
Color management processing is performed to minimize the effect of imaged colors, uneven lighting, shadows, and other factors through the provision of a dedicated color chart on the mount onto which the immunochromatography test paper is attached, thereby improving analysis accuracy. It is also possible to output an error alert in the event of an imaging issue. Analysis efficiency can be improved by eliminating the need for conventional analysis preparation.
2) Automatic analysis improves test accuracy and efficiency
Image analysis has been fully automated, whereas previously it had to be conducted manually. This eliminates any variation in image analysis arising from the differing judgements of technicians and improves efficiency.
Verification of exosome quantification
In collaboration with DNT, TOPPAN was able to confirm that this technique can be used to digitize and quantify the amount of exosomes detected through immunochromatography.
Test Period: November 2023 to February 2024
Test details: Results of detection using Exorapid-qIC™ Immunochromatography Kit for Extracellular Vesicles were affixed to a mount with a dedicated color chart and converted into digital imagery. This image data was analyzed using CAM-FIT®, which created a calibration curve for quantification, and the results were subsequently digitized and quantified.
Each Company's role
TOPPAN
Provision of mounts with dedicated color charts and system for quantifying data through color management techniques
DNT
For the development of the quantification system, DNT (1) defined the issues surrounding quantification and (2) provided opinions from the perspective of the user. DNT is currently developing a new immunochromatography kit compatible with the quantitative system.
Future
Through the use of technology based on the patent, TOPPAN aims to contribute to work by research institutions on next-generation modalities5 for drug discovery using extracellular vesicles, and to drive the development of new detection technologies. TOPPAN will also advance research into new diagnostic technologies for the medical field to satisfy unmet medical needs6.
1. Immunochromatography
A technique that harnesses capillary action to allow a liquid to flow through a porous material, making it easier to detect and measure substances in body fluids and other samples. This method is used in test kits for influenza and COVID-19.
2. Exosome
A type of extracellular vesicle released by various types of cells. They contain proteins and nucleic acids and hold a large amount of information about the cells in which they originate.
3. Liquid biopsy
A process that detects components in blood and other body fluids to obtain information needed in the diagnosis and treatment of specific diseases. Liquid biopsies are less invasive to the human body than normal biopsies due to the use of body fluids.
4. CAM-FIT®
A cloud-based service that allows for image color correction through the imaging of the target alongside a dedicated color chart printout.
https://solution.toppan.co.jp/ds/service/colormanagementsystem.html (in Japanese)
5. Next-generation modalities
A general term used to describe a class of drugs using mechanisms that differ from conventional modalities and that are used in new treatment methods such as nucleic acid therapy, gene therapy, and cell therapy.
6. Unmet medical needs
The medical need for treatments for diseases for which no effective treatment has yet been discovered.
- Questions to ask about inkjet for corrugated packaging
- Can Chinese OEMs challenge Western manufacturers?
- The #1 Question When Selling Inkjet
- Integrator perspective on Konica Minolta printheads
- Surfing the Waves of Inkjet
- Kyocera Nixka talks inkjet integration trends
- B2B Customer Tours
- Keeping Inkjet Tickled Pink
© 2024 WhatTheyThink. All Rights Reserved.














